IN ENGLISH
IN ENGLISH  General Issues
General Issues  Gender Discrimination in Football Organizations
Gender Discrimination in Football Organizations
| Gender Discrimination in Football Organizations |
|
Lale ORTA, Ph.D. 28 September 2012
Okan University, Graduate School of Applied Sciences, Department of Sport ManagementThis study has been accepted for publication as an article for International Review of Business and Social Sciences (IRBSS) Journal September 2012 Vol.1 No.10 (ISSN: 2226-4124).
ABSTRACT
Women have encountered gender discrimination and inequalities throughout history; and their rights have always been less and their statuses have been considered lower in comparison with men. Despite the “Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women - CEDAW”, designed and adopted by the United Nations in 1979 in such a way as to enable women to actively participate in sports and physical education activities equally with men; equal opportunities for women in football have been created too late by the FIFA, UEFA and International Olympic Committee. Olimpiyat Oyunlarında erkek futbolu ilk kez 1908 yılında resmi olarak yer alırken, kadın futbolu Olimpiyat Oyunlarında ilk kez 1996 yılında yer almış ve erkeklerden 88 yıl sonra düzenlenmiştir.Men's football was officially included in the Olympic Games in 1908 for the first time, and the women's football was officially included in the Olympic Games in 1996 for the first time, i.e. 88 years later than men’s football organization.FIFA tarafından organize edilen Erkekler Dünya Kupası ilk kez 1930 yılında düzenlenirken, Kadınlar Dünya Kupası tam 61 yıl sonra, 1991 yılında ilk kez düzenlenmiştir.Men's World Cup was organized by FIFA in 1930 for the first time, and Women's World Cup was organized in 1991 i.e. 61 years later.Kadınlar Dünya Kupası ile erkekler Dünya Kupası organizasyonu arasında 61 yıl fark vardır.There are 61 years between Women's World Cup organizations and Men's World Cup organizations. FIFA tarafından 20 Yaş Altı erkek futbol organizasyonları ilk kez 1977 yılında yapılırken, kadınlarda ilk kez 2002 yılında düzenlenmiştir.The first Under-20 Men's Football organization was made in 1977, and the first Under-20 Women’s Football organization was made in 2002. 20 Yaş Altı kadınlar ve erkekler futbol organizasyonları arasında 25 yıl ara vardır. There are 25 years between the first Under-20 Men's Football organizations and the first Under-20 Women’s Football organizations. 17 Yaş Altı erkek futbol organizasyonları ilk kez 1985 yılında düzenlenirken, kadınlar için ilk kez 2008 yılında organize edilmiştir.The first Under-17 Men's Football organizations were made in 1985, and the first Under-17 Women’s Football organization was made in 2008.17 Yaş Altı kadınlar ve erkekler futbol organizasyonları arasında 23 yıl fark vardır. There are 23 years between the first Under-17 Men's Football organizations and the first Under-17 Women’s Football organizations.
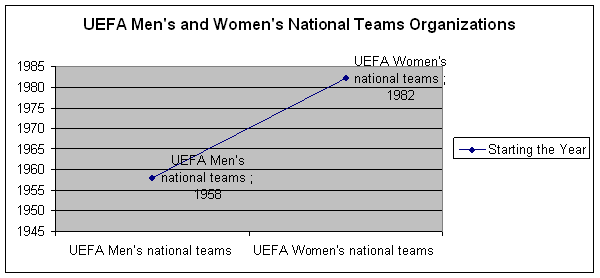
The first Men's European Championship was organized by UEFA in 1958, and Women's European Championship was held in 1982. There are 24 years between the Men's and Women’s European Championship organizations. The first men's club team organization was made in 1955, and the first Women's European Championship was held 46 years later in 2001. Men’s Champions League was started by UEFA in 1992, and Women's Champions League was started in 2008, instead of Women's Cup. There are 16 years between Men’s Champions League and Women's Champions League.
For the first time, the Youth Olympic Football organizations were made by FIFA for both men and women in the same year, without gender discrimination. This shows the fact that today equal plans are being made for women and men organizations.
Keywords: FIFA, UEFA, Football Organizations, Gender Discrimination
INTRODUCTION
The condition for a sustainable anthropocentric development is the creation of a partnership between women and men based on equality (Sport and Gender, 2005).
As one of the social problems, gender discrimination emerges as a discrimination against women. Women have encountered gender discrimination and inequalities throughout history. Their rights have always been less and their statuses have been considered lower in comparison with men (Demirbilek, 2007).
The data obtained from statistical studies shows that women are in a more disadvantaged position in terms of gender-based occupational discrimination. This adversely affects the position of women in the labor market as well as their social variables such as education, income, health, and sports; and the transfer of these adverse effects to the next generation leads to the emergence of gender inequality (Parlaktuna, 2010). According to the results of the survey made, the levels and ways of the women’s participation in sports, which are lower and different in comparison with men, as well as their disadvantageous position in sports environment are attributed to many factors. These are expressed with the assertions that; intense participation in the competition sports may cause women to face problems in child rearing; contact-based sports activities may pose danger for women's reproductive organs and breasts; women have slimmer bone structure than that of men, and therefore the risk of injury is higher for women; intense participation in sports may cause menstrual problems leading to emotional problems; therefore women should not be included in the environments, which cause emotional and physical overstrain (Koca & Bulgu, 2005).
Inequality of women before the law prompted them to claim their political rights, with intent to gain and legalize the equality (Bebel, 1978).
The 1st Women's Rights Convention was held in New York in 1848 In the convention attended by 260 women and 40 men, it was advocated that women should have equal rights as well as right of voting (Bensadon, 1994).
In many democratic communities, the requirements of women, who want to gain their legal and economic independence, was tried to be met, by means of detailed regulations intended for eliminating the unrighteousness (Bensadon, 1994).In 19th century, many women acquired a distinguished position in the branch of art, literature, astronomy, mathematics, and science. In North America, they particularly come into prominence in the fields of social sciences and social innovation (Michel, 1994.)
Finland was the first European country that adopted the women's rights, with the Statute of the State Assembly, dated June 1, 1906. At that time, Finland was a Russian principality. With the amendment in the Constitution of Denmark in 1915, the women's right to vote was adopted in Denmark. The dictatorial regimes, which ruled in Germany and Italy during the period between the 1930s and the end of World War II in 1945, caused the women's rights to regress in these countries (Bensadon, 1994).
The United Nations declared the period between 1975 and 1985 as the "woman’s ten years", and took the lead for the three major international conference done in this period. The United Nations focusing on the inequality between women and men in all areas adopted the convention on the "Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women," in 1979 (Koray, 1994).
Clause ‘g’ of Article 10 in Section 3 of the United Nations’ Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women has been designed in such a way as to enable women to actively participate in sports and physical education activities equally with men (Cedaw, 1979).
Our study is intended for ascertaining whether there is equality between the organizations made for men’s and women’s football. In Football, the International Federation of Association Football is the most authoritative body in the organization of international matches and tournaments (Orta, 2000). Men's World Cup was organized by FIFA in 1930 for the first time, and Women's World Cup was organized in 1991 i.e. 61 years later (Orta, 2000).
Union European Football Association-UEFA is the most authoritative organ that organizes international football matches and tournaments in European continent. The first Men's European Championship was organized by UEFA in 1958, and Women's European Championship was organized in 1982, ie., 24 years later (Orta, Akşar, Beşiktaş, 2012).
METHOD
In this study, analyses and examinations were made on the men’s and women’s football organizations of FIFA and UEFA, which are the governing bodies in the world football European football respectively; and some factors were discussed and compared with each other. The data obtained from the comparisons were calculated and interpreted by statistical methods. Horizontal approach was applied for comparisons. The men’s and women’s football organizations compared in horizontal approach were discussed. Accordingly, the followings comparisons were made; - The men's football organizations made by FIFA at the level of national teams; and the women's football organizations made by FIFA at the level of national teams, - The men's football organizations made by FIFA at the level of club teams; and the women's football organizations made by FIFA at the level of club teams - The men's football organizations made by UEFA at the level of national teams; and the women's football organizations made by UEFA at the level of national teams - The men's football organizations made by UEFA at the level of club teams; and the women's football organizations made by UEFA at the level of club teams.
The data required in this study are based on printed and internet sources. For this reason, the resources related to the football organizations made by FIFA and UEFA were researched
FINDINGS
Football that was included in the Olympic Games in 1900 and 1904 as a demonstration sport was the first the first team sport in Olympics. The first official Olympic Football Tournament was made 1908 in London Olympics, in which eight teams competed (www.olympic.org).
World Cup Finals, which are organized in every four years, was held in 1930 for the first time. FIFA U-20 World Cup was organized under the name of "World Youth Championship" in 1977, for the first time. FIFA U-17 World Cup was organized in 1985, for the first time. And FIFA Futsal (indoor football) was organized in 1989, for the first time. Beach football officialized in the 1990s after determination of its specific rules began to be organized under the name of “FIFA Beach Football World Cup” as from 2005, as a FIFA organization. The organization made for the first time under the name of "King Fahd Cup" in Saudi Arabia in 1992 was included in the structure of the organization FIFA in 1995, and was named "FIFA Confederations Cup". The first Youth Olympic Football Tournament participated by national under-17 teams and hosted by Singapore was held in 2010 (see www.fifa.com).
The football organizations made by FIFA at the level of men's national teams and their commencement years are shown in Table 1 and Figure 1.
Table 1. FIFA Men's National Team Football Organizations and Their Commencement Years
Figure 1. FIFA Men's National Team Football Organizations and Their Commencement Years "FIFA Women's World Cup" Football held in every four years at the level of men's national teams was organized in 1991 for the first time. Women's football was included in Olympics in Atlanta for the first time in 1996, with the participation of 8 teams. The first biennial "FIFA U-20 Women's World Cup" and "FIFA U-20 Women's World Cup" were organized in 2002 and 2008, respectively. The "1st Youth Olympic Games" participated by under-15 girls was organized in 2010 for the first time, and 6 teams competed (see www.fifa.com).
The football organizations made by FIFA at the level of women's national teams and their commencement years are shown in Table 2 and Figure 2.
Table 2. FIFA Women's National Team Football Organizations and Their Commencement Years
Figure 2. FIFA Women's National Team Football Organizations and Their Commencement Years
The commencement years of the men’s and women's football organizations made by FIFA are shown in Table 3.
Table 3. The commencement years of FIFA Men’s and Women's World Cup Organizations
The commencement years of the men’s and women's football organizations at the level of national teams in Olympic Games are shown in Table 4.
Table 4. The commencement years of the men’s and women's Olympic football organizations
The commencement years of the FIFA U-20 men’s and women's football organizations at the level of national teams are shown in Table 5.
Table 5. FIFA U-20 World Cup Organizations
The commencement years of the FIFA U-17 men’s and women's football organizations at the level of national teams are shown in Table 6.
Table 6. FIFA U-17 World Cup Organizations
The commencement years of FIFA Youth Olympic Football Organizations for national men’s and women’s teams are shown in Table 7.
Table 7. The commencement years of Youth Olympic Football Tournaments
Only two football organizations are organized by FIFA at the level of clubs. FC Blue Stars/FIFA Youth Cup organized traditionally by the club Zurich in every year since 1939, which is attended by new skilful people as candidate for professionalism in the world football was taken over by FIFA in 1991, and then it began to be organized under the name of “FIFA Youth Cup”. FIFA Club World Cup was organized for the first time in 2000, under the name of "FIFA World Club Championship", with the participation of 6 continental champion clubs. It could not been organized between 2000 and 2005. Its name was changed to "FIFA Club World Cup (see www.fifa.com).
The commencement years of the football organizations for men's club teams made by FIFA are shown in Table 8 and Figure 3.
Table 8. The football organizations for men's club teams made by FIFA
Figure 3. The organizations for men's club teams made by FIFA As the first football organization made by UEFA in 1958 at the level of national teams, "European Cup" could not attract the expected attention in the first year due to insufficient participation. The initial name of the cup was “Henry Delaunay”, and then it was changed to "European Nations Cup", and finally to "European Football Championship" in 1965. Since 1976, UEFA Under-23 Football Championship has been organized as "Under-21". The name of the championship that began to be organized under the name of International Youth Football Tournament between 1948 and 1980 was changed to U-18 European Championship in 1980, and to U-19 European Championship. U-17 European Championship was organized in 1980 for the first time, under the name of U-16 European Championship. European Inter-Regional Junior Championship was organized in 1978 for the first time (see www.uefa.com).
The football organizations made by UEFA at the level of men's national teams and their commencement years are shown in Table 9 and Figure 4.
Table 9. The football organizations of UEFA at the level of men's national teams
Figure 4. The football organizations of UEFA at the level of men's national teams and their commencement years The European Women's Football Competitions commenced in 1982 was named European Women's Championship in 1989. European Women's Championship organized in every four years is organized with the participation of 16 teams. U-18 Women's Championship was organized in 1997–1998 Football Season, for the first time. Denmark was the first champion of the championship, which is held every year. In 1998-1999 football season, its name and competition format were changed, and it become U-19 (under age 19) Women’s Championship (see www.uefa.com).
The football organizations made by UEFA at the level of women's national teams and their commencement years are shown in Table 10 and Figure 5.
Table 10. The football organizations of UEFA at the level of women's national teams and their commencement years
Figure 5. The football organizations of UEFA at the level of women's national teams and their commencement years The football organizations made by UEFA at the level of men’s and women's national teams and their commencement years are shown in Table 11.
Table 11. The Commencement Years of the organizations of UEFA at the level of men’s and women's national teams
“Inter-Cities Fairs Cup" participated by the teams of the cities hosting trade fairs was commenced by UEFA in 1955-1956 football season. Upon the incensement of the participation in the event, the event’s status was changed, and it was named “UEFA Cup” in 1971–1972 season. With intent to enable UEFA Cup to reach the standards of Champions League, radical changes were made in team status in 2009. As from 2009-2010 season, it began to be organized under the name of “UEFA European League”. “UEFA Champions League” was commenced in 1992–1993 season, 36 years after the organization of Champion Clubs Cup. Champions League is the most important organization among the 19 organization made by UEFA. European Cup Winners' Cup organized in 1960-1961 football season for the first time was combined with "UEFA Cup" in 1999-2000 football season, by considering the decreasing interest of the people caused by the large number of the matches played at the level of clubs. UEFA Intertoto Cup has been the only football organization that has not any final, champion and cup (see www.uefa.com).
The club team football organizations made by UEFA, and their commencement years are shown in Table 12 and Figure 6.
Table 12. Men’s club team football organizations made by UEFA, and their commencement years
Figure 6. Men’s club team organizations made by UEFA, and their commencement years UEFA Women's Cup attended by champion teams of the countries was organized by UEFA in 2001 for the first time. This organization was named UEFA Women's Champions League in 2009 (see www.uefa.com).
The women’s club teams football organizations made by UEFA, and their commencement years are shown in Table 13 and Figure 7.
Table 13. The Commencement years of UEFA Women's Club Teams Organizations
Figure 7. The Commencement years of UEFA Women's Club Teams Organizations The men’s and women’s club teams football organizations made by UEFA, and their commencement years are shown in Table 14.
Table 14 The Commencement years of UEFA Men’s and Women's Club Teams Organizations
The commencement years of the football organizations of the men’s and women’s club teams made by UEFA shown in Table 15.
Table 15 The Commencement years of the Organizations of UEFA Men’s and Women's Champions League
CONCLUSION
Despite the “Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women - CEDAW”, designed and adopted by the United Nations in 1979 in such a way as to enable women to actively participate in sports and physical education activities equally with men; equal opportunities for women in football have unfortunately been created too late by the FIFA, UEFA and International Olympic Committee. The year differences determined between the men's and women's football organizations are as follows:
Men's football was officially included in the Olympic Games in 1908 for the first time, and the women's football was officially included in the Olympic Games in 1996 for the first time, i.e. 88 years later than men’s football organization (Figure 8).
Figure 8. The Commencement Years of Men’s and Women’s Olympic Football Organizations Men's World Cup was organized by FIFA in 1930 for the first time, and Women's World Cup was organized in 1991 i.e. 61 years later.Kadınlar Dünya Kupası ile erkekler Dünya Kupası organizasyonu arasında 61 yıl fark vardır.There are 61 years between Women's World Cup organizations and Men's World Cup organizations (Figure 9).
Figure 9. The Commencement Years of Men’s and Women’s FIFA World Cup Organizations The first Under-20 Men's Football organization was made in 1977, and the first Under-20 Women’s Football organization was made in 2002. 20 Yaş Altı kadınlar ve erkekler futbol organizasyonları arasında 25 yıl ara vardır. There are 25 years between the first Under-20 Men's Football organizations and the first Under-20 Women’s Football organizations (Figure 10).
Figure 10. FIFA U-20 World Cup Organizations The first Under-17 Men's Football organizations were made in 1985, and the first Under-17 Women’s Football organization was made in 2008. 17 Yaş Altı kadınlar ve erkekler futbol organizasyonları arasında 23 yıl fark vardır. There are 23 years between the first Under-17 Men's Football organizations and the first Under-17 Women’s Football organizations (Figure 11).
Figure 11. FIFA U-17 World Cup Organizations For the first time, the Youth Olympic Football organizations were made by FIFA for both men and women in the same year, without gender discrimination (Figure 12).
Figure 12. The Commencement Years of the Youth Olympic Football Organizations The first Men's European Championship was organized by UEFA in 1958, and Women's European Championship was held in 1982. There are 24 years between the Men's and Women’s European Championship organizations (Figure 13).
Figure 13. The Commencement Years of the UEFA Organizations for Men’s and Women's National Teams The first men's club team organization of UEFA was made in 1955, and the first Women's European Championship was held 46 years later in 2001 (Figure 14).
Figure 14. The Commencement Years of the UEFA Organizations for Men’s and Women's Club Teams Men’s Champions League was started by UEFA in 1992, and Women's Champions League was started in 2008, instead of Women's Cup. There are 16 years between Men’s Champions League and Women's Champions League Figure 15).
Figure 15. The Commencement Years of the UEFA Organizations for Men’s and Women's Champions League All the football events organized by FIFA and UEFA until 2010 had been made for men first. Small number of teams does not pose an obstacle for organizing an event, and besides, it reflects the approaches and perspectives regarding the subject. For those who assert that there is not adequate number of teams in women’s football, we can give some examples such as the facts that men’s football was included in the Olympic Games with 3 teams, between the years 1900 and 1904, even if they were for the purpose of demonstration; football officially participated in the games with 6 teams in 1908; and the first World Cup was held with only 13 teams.
For the first time, the Youth Olympic Football organizations were made by FIFA in 2010 for both men and women in the same year, without gender discrimination. This shows the fact that today equal plans are being made for women and men organizations.
In addition, FIFA and UEFA are required to utilize and distribute all the economical sources equally for men and women. The condition for a sustainable anthropocentric development in also football is the creation of a partnership between women and men based on equality.
REFERENCES
Bebel, A., (1978). Kadın ve Sosyalizm, (Çeviri:Sabiha Zekeriya Sertel), Toplum Yayınevi, İstanbul.
Bensadon, N., (1994). Başlangıcından Günümüze Kadın Hakları (Çeviri: Şirin Tekeli), Cep Üniversitesi, İletişim Yayınları, İstanbul. Cedaw, (1979). Birleşmiş Milletlerce 1979’da kabul edilen “Kadınlara Karşı Her Türlü Ayrımcılığın Önlenmesi Sözleşmesi”.
Demirbilek, S., (2007). Cinsiyet Ayrımcılığının Sosyolojik Açıdan İncelenmesi. Finans Politik & Ekonomik Yorumlar, 44, ss. 12-25
Koca, C., & Bulgu, N. (2005). Spor ve toplumsal cinsiyet: Genel bir bakış. Toplum ve Bilim Dergisi, 103.
Koray, M., (1994). Türkiye’de Kadınlar, Türkiye Sosyal Ekonomik Siyasal Araştırmalar Vakfı, Türkiye’nin Sorunları Dizisi-4, Yeni Yüzyıl Kitaplığı.
Michel, A., (1994). Feminizm (Çeviren: Şirin Tekeli), Cep Üniversitesi, İletişim Yayınları, Preses Universitaires de France.
Orta, L., (2000). “FIFA Dünya Kupası Finallerinin Analitik Olarak İncelenmesi”, Gazi Üniversitesi BESYO 1. Ulusal Beden Eğitimi ve Spor Bilimleri Kongresi, Cilt 2, s.227-239, 2000, Ankara. Orta, L., (2000). “Futbolda Bayanlar Dünya Kupası ile Erkekler Dünya Kupasının Karşılaştırılarak İncelenmesi”, Gazi Üniversitesi BESYO 1. Ulusal Beden Eğitimi ve Spor Bilimleri Kongresi, 26-27 Mayıs 2000, Ankara.
Orta, L., Akşar, T., Beşiktaş, Y., (2012). Analytical Study Of The Uefa European Football Championship, İİB International Refereed Academic Social Sciences Journal, Volume: 03, Issue:07. Parlaktuna, İ., (2010). Türkiye’de Cinsiyete Dayalı Mesleki Ayrımcılığın Analizi (Analysis of Gender-Based Occupational Discrimination in Turkey), Ege Akademik Bakış, Cilt: 10, Sayı:4 Ekim 2010, ss. 1218.
Sport and Gender, (2005). Empowering Girls and Women, Chapter 4, Source: UNDP, Taking Gender Equality Seriously.
www.fifa.org
www.uefa.com
www.olympic.org
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Degerli yazarimiz Lale Orta Pazartesi, 14 Kasım 2011.
YAZARIN DIGER YAZILARINI GORMEK ICIN TIKLAYIN
- Kadın Futbolunun Saha İçi Analizi- UEFA Kadınlar Şampiyonlar Ligi Örneği (14 Mart 2022)
- Futbolun Değişimi ve Dönüşümü (1863-2020) (16 Eylül 2020)
- Futbol Oyun Kuralları ve Teknoloji (18 Mayıs 2019)
- Sporda Kadın (06 Mart 2017)
- Futbol ve Teknoloji (26 Ocak 2017)
- Ligin 5. Haftası Deyip Geçmeyin! (30 Eylül 2016)
- Futbol ve Küfür – I (1950-1960) (14 Şubat 2016)
- Türkiye'de Kadın Futbolunun Tarihçesi (11 Eylül 2014)
- İnsan Olmak: Süleyman Seba (16 Ağustos 2014)
- 58.Sezona Merhaba Derken, İnsan Olmak: Süleyman Seba (16 Ağustos 2014)
- Ofsayta Düşenler! (23 Şubat 2014)
- Hakem Drogba'yı Neden Bekletti? (03 Şubat 2014)
- Sorun Kartlarda... (28 Kasım 2013)
- Futbol Oyun Kuralları’nda Neler Değişti? (25 Ağustos 2013)
- Selçuk Yula (07 Ağustos 2013)
- Futbolda Kadın Olmak… (08 Şubat 2013)
- MHK Başkanı Sayın Zekeriya Alp’e Açık Mektup… (16 Ocak 2013)
- Şampiyonluğa Giden Yol… Dört Takımın Performans Analizi (2000-2013) (09 Ocak 2013)
- Süper Lig’in Kalitesi (29 Kasım 2012)
- Dört Büyük Takımın 9. Hafta Performansı (2000-2012) (05 Kasım 2012)
- Gol Atmayı Bilmiyoruz! (29 Ekim 2012)
- Gender Discrimination in Football Organizations (28 Eylül 2012)
- Futbol Organizasyonlarında Cinsiyet Ayrımcılığı (28 Eylül 2012)
- Fenerbahçe - Trabzonspor Rekabeti (23 Eylül 2012)
- Türkiye Birinci Ligi’nin Tarihsel Gelişimi - II (18 Eylül 2012)
- Milli Takım Analizi (2000-2012) (10 Eylül 2012)
- Türkiye Birinci Ligi’nin Tarihsel Gelişimi - I Türkcell Süper Lig’e Uzanan Yol… (27 Ağustos 2012)
- 'Asessment Of The Football Referees’ Interpretations On The Laws Of The Game (13 Ağustos 2012)
- 'Asessment Of The Football Referees’ Interpretations On The Laws Of The Game (13 Ağustos 2012)
- Futbol hakemlerinin Kural Yorumlarının Ölçülmesi (13 Ağustos 2012)
- Futbol Oyun Kuralları’nda Neler Değişti? (03 Ağustos 2012)
- Avrupa Futbol Şampiyonası (20 Mayıs 2012)
- Genel Kurul’un Adı Yok! (09 Mayıs 2012)
- Futbolun Geleceği - 11 Vazgeçilemez Değer (24 Nisan 2012)
- Türk Futbolunun Analizi (2006–2012) (16 Nisan 2012)
- Kesin Ofsayt (!) Tarihçesi… (09 Nisan 2012)
- Futbolcunun Adı Yok! (02 Nisan 2012)
- Taraftar Farkı (26 Mart 2012)
- Kadın Taraftarlar (19 Mart 2012)
- Futbol Organizasyonlarının Tarihsel Gelişimi II: FIFA Organizasyonları (12 Mart 2012)
- FIFA KADINLAR DÜNYA KUPASI FİNALLERİNİN ANALİTİK OLARAK İNCELENMESİ (05 Mart 2012)
- Futbolun Delege Yapısı ya da Türk Futbolunun Temeli Sağlam mı? (27 Şubat 2012)
- Çözüme Giden Yol… (21 Şubat 2012)
- Darağacının Işıltılı Gölgesi… (13 Şubat 2012)
- Futbolda Kriz Yönetimi (06 Şubat 2012)
- Futbol Organizasyonlarının Tarihsel Gelişimi - I (29 Ocak 2012)
- Çaresizliğin Dayanılmaz Arayışı! (23 Ocak 2012)
- Şair Ruhlu Kramponlar (16 Ocak 2012)
- Kadın Sporcu Aranıyor! (09 Ocak 2012)
- Var Olmanın Dayanılmaz Çaresizliği ! (30 Aralık 2011)
- Şikenin Ayak İzleri… ( III) (26 Aralık 2011)
- Şikenin Ayak İzleri… ( II) (20 Aralık 2011)
- Şikenin Ayak İzleri… ( I ) (15 Aralık 2011)
- Şanslar Müsavi Favori Yok! (05 Aralık 2011)
- Akaretlerden Maçka'ya...Maçlardaki Yaşanmışlıklara... (30 Kasım 2011)
- Futbol Oyun Kurallarının Tarihsel Gelişimi (25 Kasım 2011)
- DÜNYADA VE TÜRKİYE’DE FUTBOL HAKEMLİĞİNİN BAŞLANGICI VE GELİŞİMİ (21 Kasım 2011)
|
Neden Futbol Ekonomisi?
www. Futbolekonomi.com’un vizyon ve misyonu temel olarak Futbol Ekonomisi Stratejik Araştırma Merkezi’nin (FESAM) vizyon ve misyonuna paralel ve aynı düzlemdedir.
Bu bağlamda temel misyonumuz: Futbolun yerel ve küresel makro özelliklerini incelemek ve yeni yapısal modeller önermek; bu kapsamda entelektüel gelişimi hızlandırmak ve buna ilişkin referans olabilecek bir database oluşturmak ve bunu tüm futbol araştırmacılarının emrine sunmak... Bu amaçla yapılan çalışmaları yayımlamak; gerekli her türlü bilimsel futbol araştırma ve geliştirme projelerine entelektüel anlamda destek vermek.
Temel Vizyonumuz: Önerilen yeni modellerin gerçekleştiğini görmektir. |
|
|
|
Yazar Tuğrul Akşar,
|
Spor Endexi
|
16/04/2024 |
Kapanış | Günlük Değişim % |
|
| BİST 100 |
9.707,13 |
-1,09 |
|
| |
BJKAS |
77,15 |
+3,28 |
| |
FENER |
96,80 |
+5,22 |
| |
GSRAY |
6,92 |
+0,44 |
| |
TSPOR |
1,59 |
-1,85 |
| SPOR ENDEKSİ |
4.847,33 |
-0,18 |
|
Son Yayınlananlar
- Futbol Yöneticilerine Açık Mektup
- İsmail Kartal Skoru Biliyor ama Sonucu Bilmiyor
- Trabzonspor'a HES Değil, Gol Lazım
- İstediğimiz Hakem
- TFF'de İmza Savaşları
- Prof.Dr. Sebahattin Devecioğlu: "Türk Futbolunu Tüm Futbol Paydaşlarıyla Birlikte Tutku, Güven ve Adaletle Yönetmeye Adayım."
- Kupanın Adı Süper, Geride Bıraktıkları ise…
- Amigo Başkanlıktan Mızıkçılığa…
- FIFA'nın Müdahale Yetkileri
- Futbol Endüstrisi, Mendes ve Montella
Yazarlar
Videolar
Tuğrul, Tuğrul Akşar, Pusula, Ekonomi, Futbol, Futbol Ekonomi, Mali,VİDEONUN DEVAMI VE DİĞER VİDEOLAR İÇİN TIKLAYIN.İstatistikler
İçerik Tıklama Görünümü : 39788203TRENDYOL SÜPER LİG 2023-2024 SEZONU
| Sıra | TAKIMLAR | 0 | G | B | M | A | Y | AV | P |
|
Galatasaray | 32 | 28 | 3 | 1 | 73 | 20 | 53 | 87 |
| 2 | Fenerbahçe | 32 | 27 | 4 | 1 | 85 | 28 | 57 |
85 |
| 3 | Trabzonspor | 32 | 16 | 4 | 12 | 54 | 42 | 12 | 52 |
| 4 | Beşiktaş | 32 | 14 | 6 | 12 | 42 | 38 | 4 | 48 |
| 5 | Rizespor | 32 | 14 | 6 | 12 | 43 | 47 | -4 | 48 |
| 6 | Başakşehir | 32 | 13 | 7 | 12 | 42 | 38 |
4 |
46 |
| 7 |
Kasımpaşa |
32 | 13 | 7 | 12 | 55 | 57 | -2 | 46 |
| 8 | Sivasspor | 32 | 11 | 11 |
10 |
38 | 43 | -5 | 44 |
| 9 | Antalyaspor | 32 | 10 | 12 | 10 | 36 | 37 | -1 | 42 |
| 10 |
Alanyaspor |
32 | 10 | 12 | 10 | 41 | 46 | -5 | 42 |
| 11 | AdanaDemir | 32 | 9 | 13 | 10 |
48 |
43 | 5 | 40 |
| 12 | Samsunspor | 32 | 10 | 8 | 14 | 36 | 42 | -6 | 38 |
| 13 | Ankaragücü | 32 | 8 | 13 |
11 |
40 | 41 | -1 | 37 |
| 14 | Kayserispor | 32 | 10 | 10 | 12 | 36 | 45 | -9 | 37 |
| 15 | Konyaspor | 32 | 8 | 12 | 12 | 34 | 45 | -11 | 36 |
| 16 | Hatayspor | 32 |
7 |
12 | 13 | 36 | 44 | -8 | 33 |
| 17 | Gaziantep | 32 | 8 | 7 | 17 | 35 | 50 | -15 | 31 |
| 18 | Karagümrük | 32 | 7 | 9 | 16 | 35 | 41 | -6 | 30 |
|
19 |
Pendikspor | 32 | 7 | 9 | 16 | 36 | 64 | -28 | 30 |
|
20 |
İstanbulspor | 32 | 4 | 7 | 21 | 25 | 59 | -34 | 16 |
Okur Yazar
|
Yazılarınızı info@futbolekonomi.com adresine gönderebilirsiniz. |
Annual Review of Football Finance 2023
Deloitte Sports Grup'un Avrupa Futbol Finansmanına ilişkin 32. kez düzenlediği yıllık futbol finans raporuna göre, Avrupa futbol pazarı 2021 - 22 sezonunda bir önceki yıla göre %7 büyüyerek 29.5 Milyar Euro büyüklüğüne ulaştı. Rapora ulaşmak için tıklayınız
Deloitte Money League - 2024
Deloitte Money League Raporunu 27. kez yayınladı. Rapora göre Avrupa'nın en zengin 20 kulübünün 2022-23 sezonunda gelirleri toplam 10.5 Milyar Euro'ya ulaştı. Raporu okumak için tıklayınız.
UEFA Kulüp Finans&Yatırım Raporu 2024
UEFA Kulüp futbolunun finansal durumları ve yatırımlarına ilişkin yıllık görünüm ve benchmark raporunu yayınladı. Okumak için tıklayınız
Yirmidördüncü Deloitte Money League raporuna göre Barcelona'nın 715.1 Milyon Euro'luk geliriyle ilk sırada yer aldığı, tamamı merkez lig kulüplerinden oluşan ve bir önceki yıla göre gelirleri %12 azalan Para Ligi raporunu okumak için tıklayınız
Avrupa Futbolunun patronu UEFA’nın gelirleri 5.7 Milyar Euro’ya Ulaştı. Raporu okumak için tıklayınız.
UEFA’nın 2023’te yayınladığı en son Kulüp Lisanslamaya İlişkin Karşılaştırma raporuna göre kulüpler Pandemi döneminde 7.3 Milyar Euro zarar ettiler. UEFA raporu, Avrupa kulüp futbolunun endişe verici bir resmini çiziyor. Raporu okumak için tıklayınız.
|
Türk futbolunun gelirlerinin ve ekonomik görünümünün mercek altına alındığı Futbol Ekonomi Raporu – EkoLig'in dördüncü sayısı yayınlandı. Süper Lig’in 2017-2018 sezonu sonunda 3,2 milyar TL olan geliri, 2018-19 sezonunda 4,2 milyar TL’na ulaştı. Bkz.
|
| |
|
The European Club Footballing Landscape 2022
|
|
“Ekospor’un aylık bültenlerinden haberdar olmak için tıklayınız” |
| |
|
''Taraftar Algısına Göre Türkiye Süper Ligi Marka Değerini Etkileyen Faktörlerin ve Marka Değeri Boyutlarının Değerlendirilmesi'' Prof. Dr. Musa PINAR öncülüğünde yapılan bu araştırmayı okumak için tıklayınız.”
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Futbolda Endüstriyel Denge ve Başarı Üzerine Futbolun Endüstriyel gelişimi, kulüplerin sportif ve iktisadi/mali yapılanışını derinden etkiliyor. Dorukhan Acar’ın Kurumsal Yönetim temelli yaklaşımı ile "Futbolda Endüstriyel Denge ve Başarı"yı okumak için tıklayınız”
|
| |
|
Türkiye'de Kadın Futbolunun Gelişimi ve Günümüzdeki Durumu
Dr. Lale ORTA’nın Kadın Futboluna Entelektüel Bir Yaklaşım Sergilediği makalesi için tıklayınız.”
|
|
İngiliz Futbolunda Kurumsal Yönetişim Üzerine
|
“Money scorring goals”, Gerçekten de “Para Gol Kaydedebiliyor mu? “Euro 2012’nin olası ekonomik etkilerini |
Futbolda Finansal Sürdürülebilirlik Kapsamında ''Finansal Fair Play Başa Baş Kuralı ve Beşiktaş Futbol Kulübü Üzerinde Bir Uygulama
|